Introduction
Tapping a fiber optic cable without being detected isn’t trivial but has been done since the mid-1990s. It is possible to intercept an optical signal because of the high transmission margins used to avoid problems (dust, bending) and due to the use of standard distance optics (10 km, 20 km, etc.).
The IT staff typically does not check reports of short intervals of downtime because of the high investigation costs or investigate changes in power variations because of they are not monitored for changes. Fiber has long been viewed as intrinsically secure, but this just isn’t the case—commercial fiber clamps exist, and fiber interception results in such insignificant signal loss that it goes undetected.
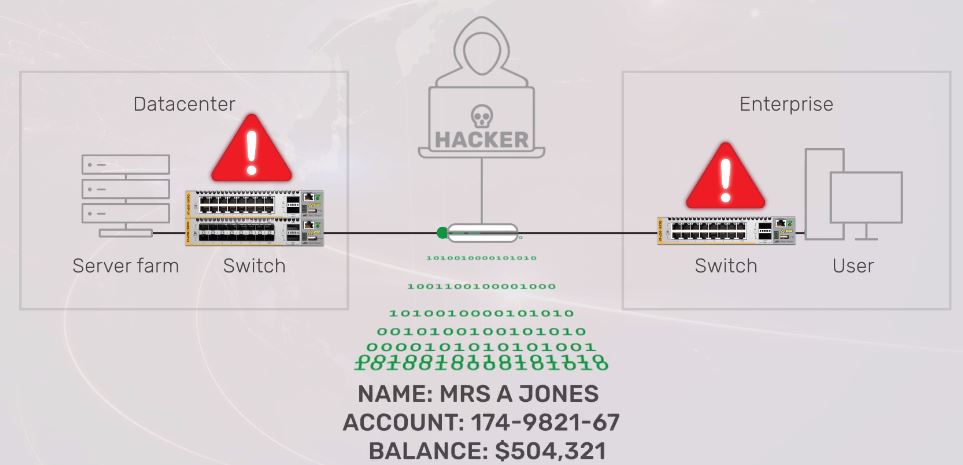
An innovative technology pioneered by Allied Telesis, our patented Active Fiber Monitoring (AFM), provides specialized data protection on optical links. You can enjoy nonstop, automated monitoring of all your optical fiber with no need for expensive third-party equipment.
Allied Telesis Active Fiber Monitoring
AFM works by detecting very small changes in the amount of light received on a fiber link. When an intrusion is attempted, the light level changes because some of the light is redirected by the eavesdropper onto another fiber. AFM detects this intrusion and raises the alarm. The link can then either be shut down automatically, or an operator can be alerted to manually intervene.
Benefits of using Active Fiber Monitoring
- Monitoring optical links to detect attack, no need for third party equipment.
- Detects power loss between 1 and 2 dB, minimizing false alarms.
- Polling every 5 seconds, continuous polling easily detects fiber tampering.
- Provides Alarm notification.
AFM is a standard feature on all AW+ devices and works with Allied Telesis Digital Diagnostic Monitoring (DDM) capable optical modules. For more information refer to the Data Sheet of your SFP module.
Configuring Active Fiber Monitoring
Step 1: Enable active fiber monitoring.
To configure a port to monitor received power at the default intervals and sensitivity, use the commands:
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1
awplus(config-if)# fiber-monitoring enable
Step 2: Configure actions.
To shut down the port when the alarm threshold is crossed, use the commands:
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1
awplus(config-if)# fiber-monitoring action shutdown
For more information of the Actions that can be performed by AFM, refer to the Command Reference of your device.
Step 3: Configure polling interval.
The interval for polling received optical power is 5 seconds by default and can be configured from 2 - 60s.
To poll the received power every 2 seconds instead of every 5 seconds, use the commands:
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1
awplus(config-if)# fiber-monitoring interval 2
Step 4: Configure how the baseline is calculated.
Active Fiber Monitoring calculates a baseline power level by averaging the power over multiple readings (12 by default). It compares the current power level with that baseline value to determine whether to raise an alarm.
Note: Values measured while the port is in the alarm state are never used as part of the baseline calculation.
To calculate the baseline values based on the average of the last 30 readings instead of the last 12 readings (configurable from 12-150), use the commands:
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1
awplus(config-if)# fiber-monitoring baseline average 30
Step 5: Configure sensitivity.
To configure the sensitivity of the alarm threshold, use the commands:
awplus(config)# interface port1.0.1
awplus(config-if)# fiber-monitoring sensitivity medium
We do not recommend setting sensitivity to highest level for multi-mode SFPs and high should be used with caution.
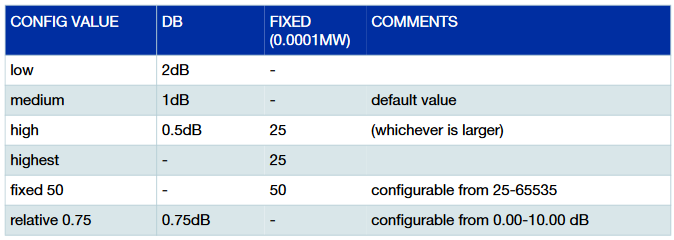
Configurable values for optical power sensitivity:
Step 6: Review configuration and status
To display the configuration and current status of active fiber monitoring, use the command:
awplus# show system fiber-monitoring
Resetting active fiber monitoring
To clear the fiber-monitoring state for an interface, including resetting the alarm and removing all baseline readings, use the command:
awplus# clear fiber-monitoring interface port1.0.1
Monitoring considerations
- To detect an attack, it is important to measure the RX power difference and not the absolute value.
- SFP resolution is about 0,0013mW. (a loss of 0.5dB at low reception threshold).
- With single mode fiber lasers, measurements are very stable, so we can use relatively low detection limits, with no false alarms.
- With less attenuation, the resolution (in dB) of the sensor is better.