Introduction
Virtual Chassis Stacking (VCStackTM) is the name given to two or more Allied Telesis switches that are configured to operate as a single switch. From a configuration and management point of view, it is as though the switches are just one device with a seamless transition from the ports of one stack member to the ports of the next.
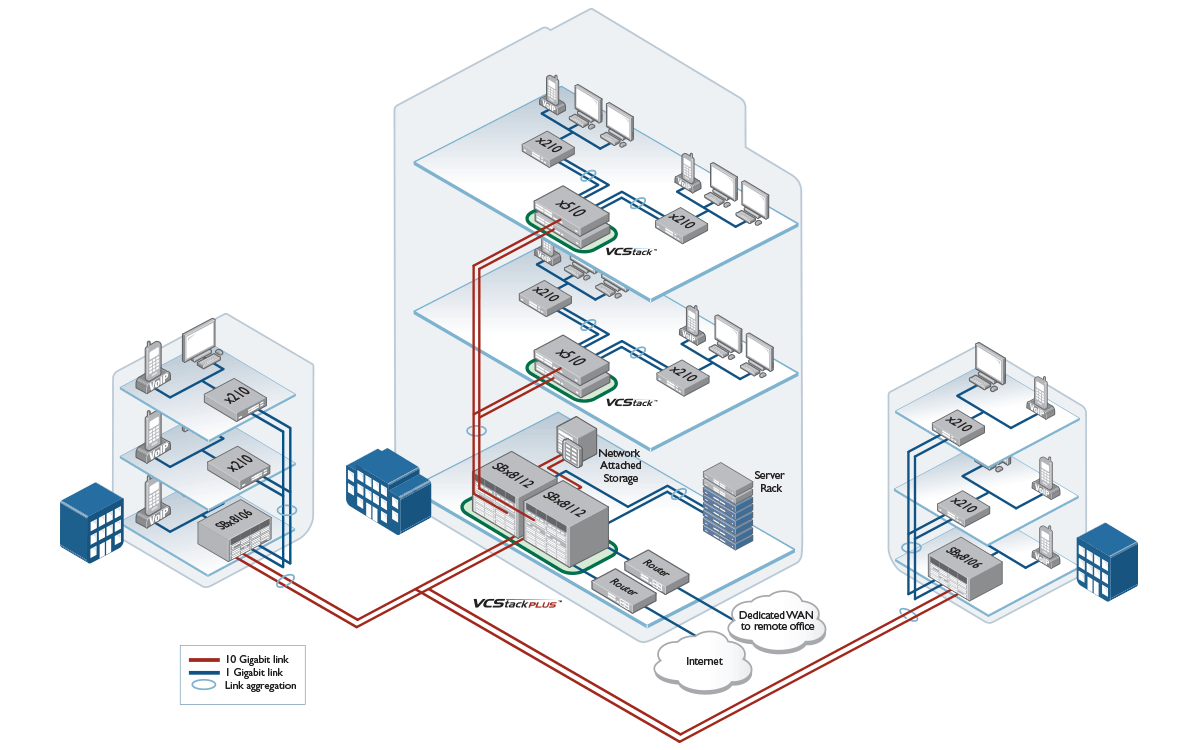
This article is not intended to be an Installation Guide, it’s a compilation of information that could be useful when implementing stacking.
For step-by-step instructions in how to set up a stack, please refer to the Installation Guide for VCStack of your device Series.
The default parameter for VCStack are:
- VCStack is enabled by default in some Series with dedicated ports for Stacking, these ports can be uses as Link ports once the stack feature is disabled with the command “no stack <stack-ID> enable”.
- The default subnet for high speed communication between stacked units via the stacking ports is 192.168.255.0/27, make sure you are not using this address range in your network. This can be changed using the CLI command “stack management subnet <ip-address>” if it causes a conflict within your network.
- The VLAN 4094 is reserved for stacking. This can be changed using the CLI command “stack management vlan <vlan id>”, as long as the new VLAN ID does not exist on the VLAN database.
Software release auto-synchronization
The effect of this feature is that when a new member joins a stack and has a software release that is different to the active master, then the active master's software release is copied onto the new member. The new member then reboots and comes up on that release.
Note: This feature can result in the new stack member downgrading its software release if the active master is running an older software version.
Occasionally you will find that the software version running on the existing stack members and the software version on the new stack member are sufficiently incompatible that the stack will not be able to auto synchronize the software version on the new member.
When this occurs, you will need to:
- Remove the new member from the stack.
- Manually upgrade the software on that switch to the same version as is running on the existing stack members.
- Re-connect the new member to the stack.
Stack virtual-mac
You must enable stack virtual-mac, in order to minimize data loss if a new stack member is required to become the VCStack master. If you dont enable a single virtual-mac for the entire stack and a new Switch become the Master, it will have a different MAC address for the entire stack, disrupting the network and causing, for example flush on the MAC address tables for Spanning-tree.
Before enabling the virtual MAC address feature, you should check that the stack’s virtual-chassis-id is not already used by another stack in the network. Otherwise the duplicate MAC addresses will cause problems for the network traffic.
The virtual-chassis-id entered will form the last 12 bits of a pre-selected MAC prefix component; that is, 0000.cd37.0xxx. The value of the ID is a decimal number in the range 0 to 4095.
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# stack virtual-chassis-id 63
This will result in a virtual MAC address of 0000.cd37.003f
The stack virtual MAC address feature is disabled by default. However, if you manually turn on stacking (by entering the stack enable command), then that enables the stack virtual MAC address feature as well.
awplus# configure terminal
awplus(config)# stack virtual-mac
Note: This command will not take effect until the switch has been rebooted.
Remote-login
This command is used only on the master in order to log onto the CLI of another stack member. In most respects the result of this is similar to being logged into the stack master. Configuration commands are still applied to all stack members, but show commands and commands that access the file system are executed locally.
awplus# remote-login <stack-ID>
Sometimes you will need to access a specific switch from the stack because its impossible for the Master to synchronize all the files due to a lack of space in the switch´s memory flash.
Note: Some commands such as ping or telnet are not available when the remote-login is used.
Checking the Health of the Stack
Use this command to display summary information about current stack members:
awplus#show stack
Virtual Chassis Stacking summary information
It is good practice to check that stack is formed correctly by not only using the show stack command, but also using "show int brief" to verify the status of the ports****
You can also display detailed information about current stack members with this command:
awplus#show stack detail
Virtual Chassis Stacking detailed information
Interface logic
In the AlliedWare Plus operating system, switch port interfaces are always referenced as portx.y.z. The first number, or "x", in the three-number port identifier is the Stack ID.
For a stand-alone switch that has never been in a stack, the ports are always numbered 1.y.z. When configuring a stack, however, there will be stack members with other stack ID values. To configure ports on these switches, use the stack ID to refer to each physical switch, for example 2.0.1, 2.0.2, 2.0.3, for the first 3 ports on a switch with stack ID 2.
Please note that when a switch is removed from a stack, it maintains its stack ID number. If it is configured as a stand-alone switch, you will need to either change the stack ID back to 1, or use the current stack ID when configuring its ports.
VCS considerations
- Master or Slave can have ID 1. The master does not necessarily have to be the unit with ID=1.
- When creating a stack, use the command “stack <stack-ID> priority <0-255>” to set the priority of the switch you want to be master for the stack, the stack member with the lowest priority value becomes the stack master.
- Stack cables must be crossed over to allow stack to form.
- The command "reload" will reboot all units in the stack. If you want to reboot only one of the units in the stack, use the command "reload stack-member x" where x is the id number of the unit you want to reboot. Note that if only the master is rebooted, it will rejoin the stack as a slave and the old slave will become the master.
- To minimize the downtime from upgrading a VCStack's software, use the command “reboot rolling”.
- VCStack is not available in Secure Mode.
- You can not do a zero touch Auto-recovery with AMF if the uplink port from the failed unit is a default Stacking port on a new device.
- Most of the Allied Telesis range of stackable devices support long-distance stacking (VCStack LD), so that stack members can be kilometers apart using SFP modules.